SD WAN has quickly become the new standard for site-to-site and site-to-cloud and data center connectivity, but its value can only be fully realized when SD WAN offers consistent, low latency performance to all enterprise locations and users. There are many causes of SD WAN performance issues, including dynamic routing that can cause packet loss and latency. Let’s first take a look at how SD WAN works to understand how its approach makes it difficult to detect and diagnose the many ways performance issues can degrade an SD WAN network.
What’s SD WAN?
A Software Defined Wide Area Network is a virtual WAN architecture which allows organizations to leverage a combination of network transport services to connect users to applications.
These transport services, usually referred to as “underlays” can be a collection of network technologies like MPLS connections, broadband internet services and GSM data connections. Each of these services have different levels of performance and reliability, which makes SD WAN performance — latency, stability, packet loss — less predictable than private networks.
SD WANs are centrally managed: network engineers use a central console to configure the logical network and the interconnections between sites, data centers and clouds. The SD WAN solution automatically orchestrates how each router dynamically handles the network traffic flows to optimize delay and costs. Decisions like choosing a certain underlay for a specific class of traffic or application is automated and transparent to the end user. This dynamic behavior is also why network operations teams have difficulty understanding performance issues, as their visibility into traffic routing across multiple underlying networks over large regions may be limited.
Why use it? The benefits of SD WAN
Organizations move from traditional WAN solutions (MPLS, layer 2 circuits) to SD WAN solutions for a variety of reasons:
- Reduce the cost of transport and bandwidth;
- Benefit from more connectivity options available in all key regions;
- Reduce latency and increase performance by avoiding centralized traffic routing to internet, SaaS and cloud services;
- Gain high availability at a reasonable cost;
- Reduce dependency on a handful of telecom service providers.
SD WAN has become the dominant WAN architecture for organizations relying massively on SaaS applications, as well as organizations with many locations (e.g. retail or manufacturing) spread across large geographies. The diversity of endpoints with different performance requirements makes SD WAN attractive, but at the same time makes managing and monitoring SD WAN performance more difficult.
How Does an SD WAN Work?
SD WAN solutions combine multiple capabilities to optimize WAN performance and cost, and automate traffic management Here are the three most important SD WAN functions that can affect network performance.
Application-aware routing
SD WAN network traffic policies are normally centrally managed, including routing, path selection, traffic classification prioritization and filtering based on application profiles. Their configuration needs to consider all business applications to make sure each gets the performance it requires across the SD WAN network.
Local internet breakout
Local Internet Breakout is a simple concept: instead of carrying internet traffic back (e.g. SaaS, web, cloud traffic) to a data center or secure gateway it is routed through a local ISP connection. This generally reduces latency, private network utilization and cost. Although the concept of a Local Internet Breakout existed before SD WAN, SD WAN has made it popular and easy to implement. The massive adoption of cloud services and SaaS applications have reinforced that trend.
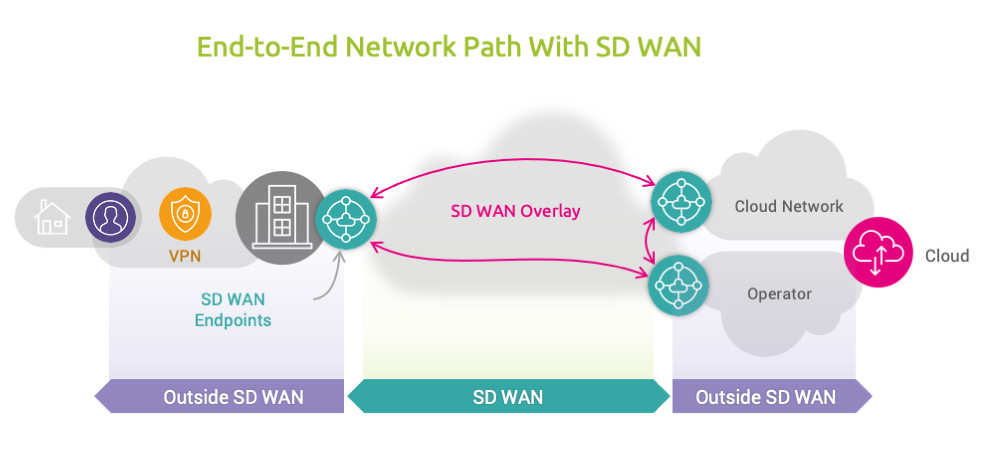
SD WAN overlays and underlays
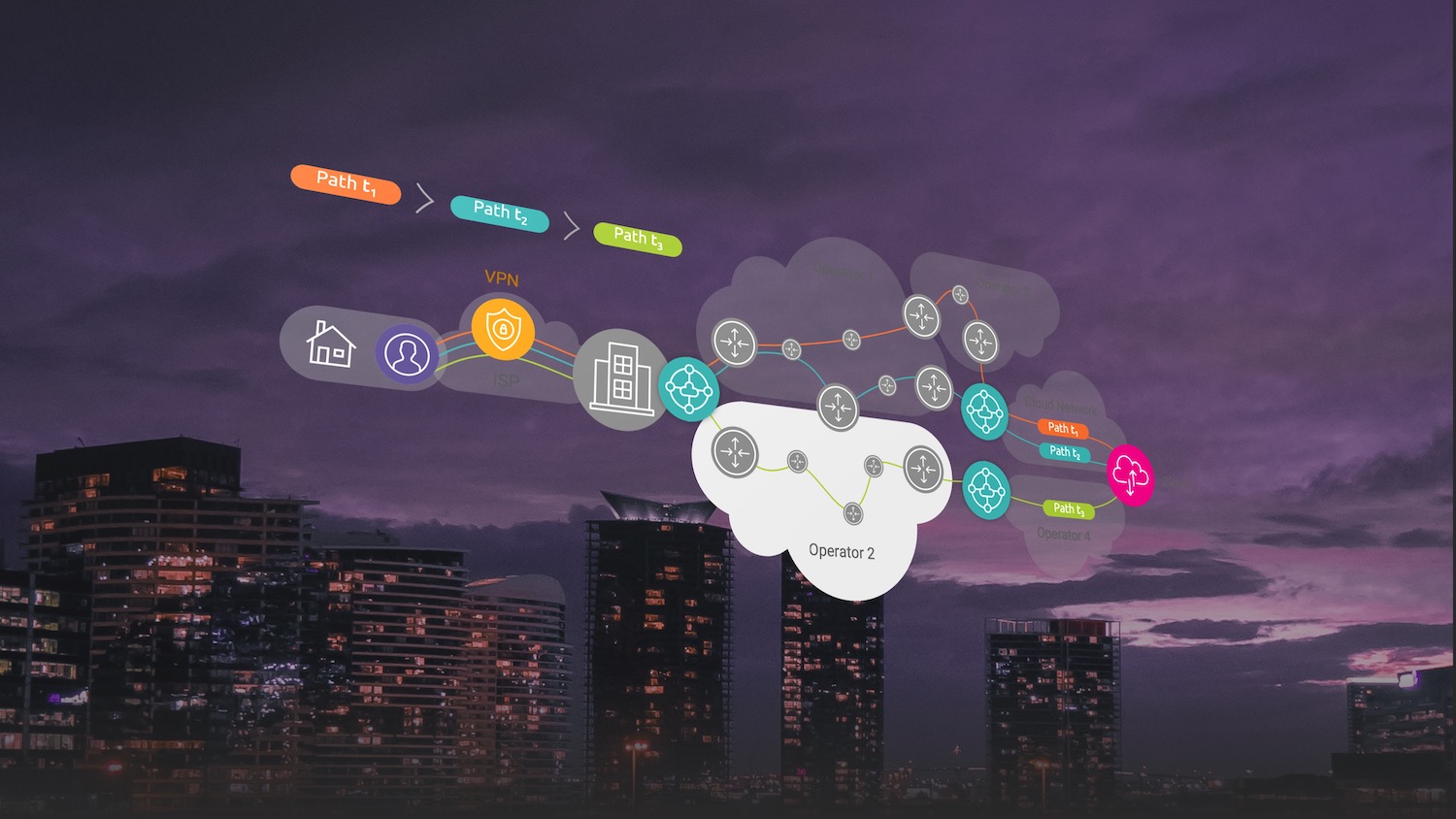
SD WAN appliances can route traffic over multiple connections (MPLS, ISPs, 4G/5G); to do so they establish tunnels (similar to a VPN tunnel) and then direct traffic through them. These tunnels are usually referred to as “Overlays”, while the underlying infrastructure (the connections themselves) are designated as “Underlays”. Both overlay and underlay routes can be dynamically routed to optimize performance or cost based. Depending on context, configuration and underlay performance this behavior can often result in the opposite outcome: unstable performance that’s difficult to diagnose. It’s important to monitor and understand the overlay and underlay network performance to optimize SD configuration for latency, throughput and reliability.
The end-to-end SD WAN path from user to application
How to Fix SD WAN Performance Issues
We’ve looked at the main factors that impact SD WAN network performance, and the ways that SD WAN works. At first glance it looks like optimizing SD WAN performance and troubleshooting SD WAN performance issues is difficult, as most network monitoring tools — and the metrics from SD WAN solutions — lack the depth and extent of coverage to isolate issues in the underlay, or to determine if network performance issues originate from the SD WAN, access or cloud-side networks.
We explain how to monitor SD WAN performance to get complete visibility into underlays and overlays in this article.
Learn how a combination of in-depth network tracing and user experience monitoring create a unique combination to help IT and network operations teams detect, diagnose and resolve SD WAN performance issues.








